ECJ Tutorial 4 - Xholon App (no GP)
What is it
This model is a Xholon version of the Tutorial 4 application included with ECJ, an evolutionary computation system written in Java. This version does NOT include genetic programming, but simply uses an already-known optimal behavior. This optimal behavior is hard-coded into a Xholon tree structure, inside the CompositeStructureHierarchy.xml configuration file.
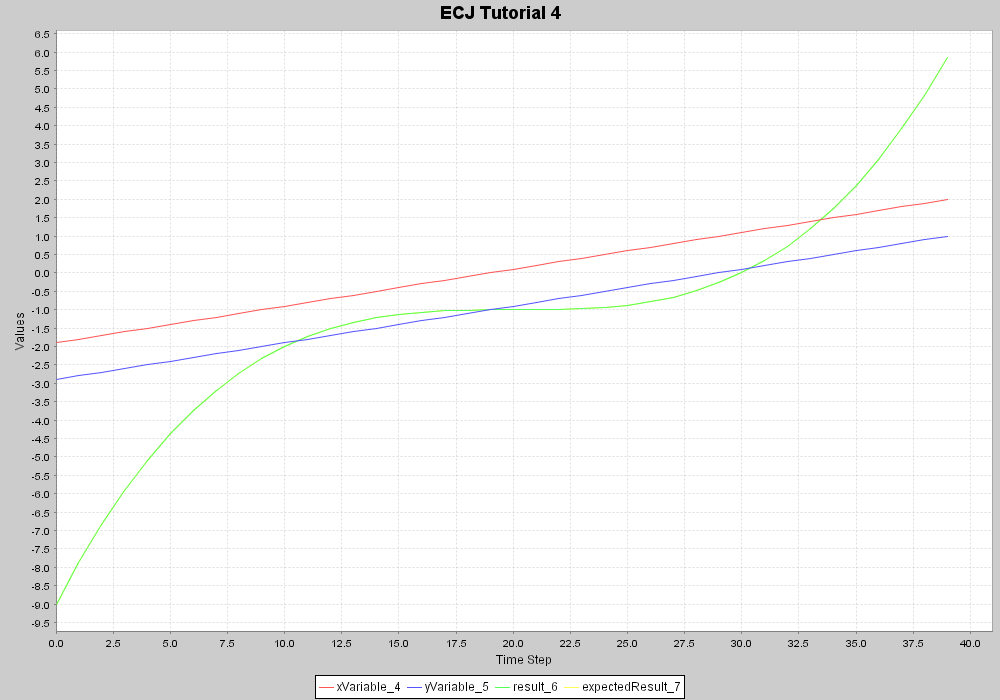
This application runs for 40 processing loops. Each time step it calculates a new result value for the function (currentX * currentX * currentY + currentX * currentY + currentY). The values of currentX, currentY, expected result and actual result are captured each time step, and optionally displayed in a chart. In this non-GP version of Tutorial 4, the expected and actual results are always the same. The Xholon tree structure that corresponds to the above function is:
<PfAdd>
<PfY/>
<PfMul>
<PfAdd>
<PfY/>
<PfMul>
<PfX/>
<PfY/>
</PfMul>
</PfAdd>
<PfX/>
</PfMul>
</PfAdd>
How to use it
Run it:
- Run the Java application through the XhnEalontro GUI (org.primordion.xholon.app.Xhn.java), and select File --> Open --> ealontro --> EcjTutorial4 --> Tutorial4_1_xhn.xml.
- Expand the Controller node in the tree.
- Press the Start node.
- If you have JFreeChart installed, and if you have selected "JFreeChart" as the value of the UseDataPlotter parameter in Tutorial4_1_xhn.xml, you should see a chart that looks like the one below. If you don't have JFreeChart installed, then change the value of UseDataPlotter to "gnuplot", and look at the results that are saved to a .csv file in the statistics folder. If you have gnuplot installed, it can read the .plt script in the statistics folder to produce a displayable .png file from the .csv file.
Things to notice
Take a look at the XML configuration files in the config/ealontro/EcjTutorial4 folder. CompositeStructureHierarchy.xml specifies initial values for the X and Y variables. Under the GeneticProgram node, it specifies the function tree that needs to be traversed to produce a correct result.
InheritanceHierarchy.xml is shared by both the GP and the NoGP versions of this application. The primitive functions (Pf) out of which the behavior is created, are divived into two types. A non-terminal primitive function has other functions as children (ex: PfAdd), while a terminal function just returns its own value (ex: PfX). Note that GeneticProgram is identified as a type of Behavior.
Look at XhTutorial4.java to learn how the result is obtained by traversing the tree.
Things to try
Run the application, but don't press Start yet. Expand the Model node, and keep expanding the nodes until you find multiValuedRegression_3. This node has four children. Click on each child to see what its value of "val" is. xVariable and yVariable have initial values of -2.0 and -3.0, while result and expectedResult don't have any values yet. Press the Step node to run the application one step at a time. After the first step, the values should have changed to: -1.9 -2.9 -9.0 -9.0 . Compare the changing values with the charted results.
Try a different pair of initial values, by editing CompositeStructureHierarchy.xml. Give XVariable and/or YVariable different initial values, something other than -2.0 and -3.0.
Extending the model
This is a simple application that can be used as a starting point for any Xholon model whose behavior is specified in a tree structure.
Xholon and Ealontro features
Specifying behavior as a tree of functions.
Displaying results in a chart.
Credits and references
Visit the ECJ website.

